EVERY DOG
Boris seems slowly to be turning into the opposition to his own party, which I suppose is not new for him. Meanwhile China also seems to be hitting an identity crisis. Neither bodes well for investors.
We apparently have a real budget due soon, but this vain Prime Minister seems bent on upstaging his own team, so we had a pile of tax rises and changes to tax law bundled out in a haphazard fashion in response to the endless (and insatiable) demands of one ministry.
A likely collision course with natural Tories
That pretty well defines bad governance, and these ad hoc excursions into major spending plans are a hallmark of waste and short termism. So, to me the investor headline should be about planning ahead for the Tory government to either fail in front of an exhausted electorate, or less plausibly given the large majority, to implode. But have no doubt that No 10 and the mass of the Tory party are now set on a collision course.
The extraordinary extravagance of the blunt furlough scheme has always been the fiscal problem, and it is hard to believe, as many bosses are clamouring for new migration to solve multiple labour problems, largely in some measure of their own making, that the government has still parked up a fair chunk of two million workers, on pretty close to full pay.
I struggle to comprehend that number in a hot summer labour market, nor do I see why employers would cling onto staff until October at which point, presumably they take a decision? Are these ghost workers? Already happily in new jobs, but having done a deal with their bosses to split the loot, their fake pay for not being? Are these people HR have forgotten or are too scared to fire? Will they really try to pick up work they put down eighteen months back, in a largely different world and probably for a now quite alien organisation?
Who knows, but the whole thing cost £67 billion (so far) and that’s what Boris needs back. I challenge anyone to give a lucid explanation of how his latest proposal “fixes” social care for the elderly. Nor to explain how in parts of the country like this, with no state care home provision anyway, it can ever be called “fair”. So, to me, it is just bunce for the ever-gaping maw of the state, and the idea, with Boris in charge, that it will ever be temporary or even accounted for, is somewhat risible.
What would “fix” social care is transparent, autonomous, local provision, not bullied by a dozen state agencies, not run by money grubbing doctors, not harried by property developers and absurd land costs, nor daft HMRC grabs on stand-by staff pay, and it needs to be highly invested in simple technology, all IT integrated with the NHS; not this crippled, secretive, subscale mess.
It is not that there is no problem, but it is as much operational as financial. A recent Bank of England paper looking at wealth distribution highlights how in retirement property comes to both dominate assets and also shrinks far more slowly with age.
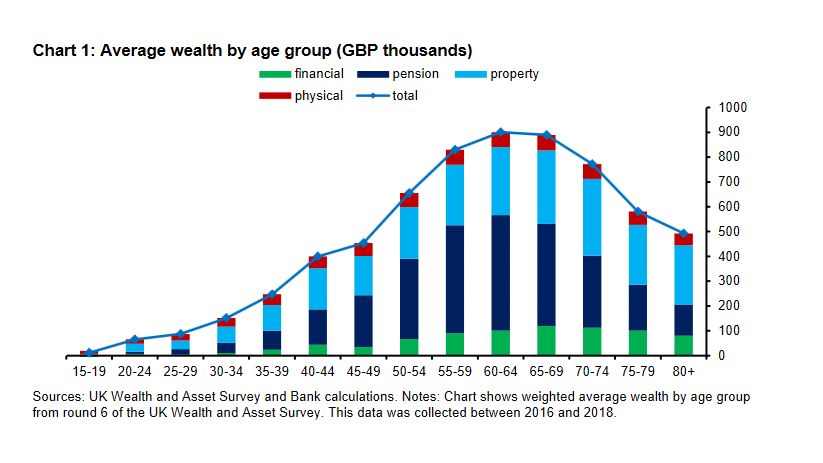
(Sourced from this speech given at the London School of Economics, by Gertjan Vlieghe, member of the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee.)
Of course, the crux here is seeing a family home as both an asset and an essential for life. That is the distortion, and this fiddling with care rules attacks the symptom, not the cause.
Can you trust a word he says?
So, now tax on income rises, a broken promise, employer tax rises, broken promise, the ‘triple lock’ on pensions is ditched, broken promise, and to top it off those working beyond normal retirement age (now 66) get a 25% tax penalty, via another broken promise. Oh, and if you are mug enough to save, then dividends will get hit too.
Again, there is a real problem but this is by no means a logical answer either: I guess the Treasury were applying heat on excess debt, and this is sand kicked back in their face, but it shows no sign of anyone solving anything. The UK has both high debt levels and no supportive currency block around it, sure France and Italy look bad, but they have Germany to help. The UK does not. Hence the anxiety.
So, Boris has had a fine Cameron-like bonfire of dozens of electoral promises; the worm turned on Cameron (and Clegg) when he couldn’t keep his word, and so it will turn on Boris. This time he won’t have Corbyn as the pantomime bete noir to bail him out. Indeed, Kier Starmer’s response linking this problem to inflated property prices is remarkably prescient, even if his typically confiscational solution is not.
These tax levels (as a % of GDP) have not been seen in fifty years, for an economy with a noticeably less effective grasp on government expenditure and a rather less globally competitive commercial base.
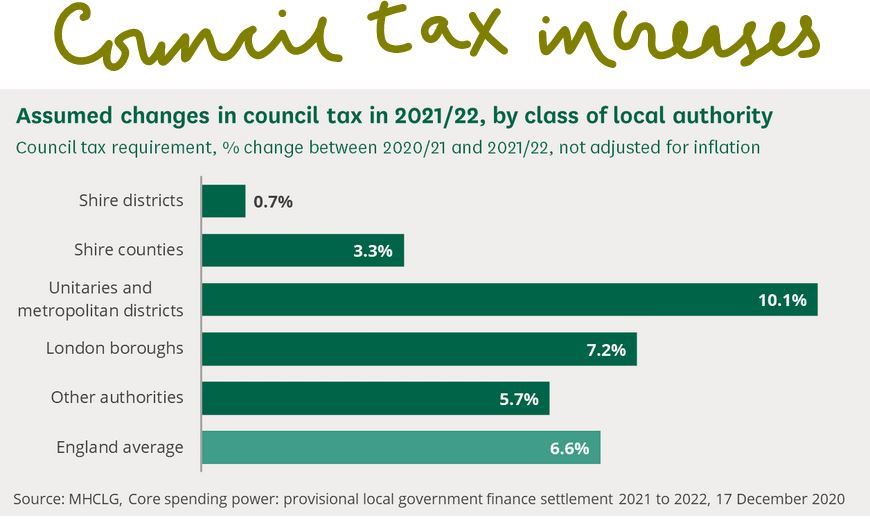
While tax rises are emerging everywhere (see below), and public service reform has become a simple money equation, need more service, spend more money, a dangerous one-way road.
Source: from this primary report
While notably, ‘buy to let’ is again left untouched. London house prices have doubled in this century, the FTSE 100 has moved from circa 6800 at its late 1999 peak to 7030 now and remains below pre-pandemic levels. So clearly this is not the time to hit the investors in jobs and business, who have had a 5% nominal gain (that is a 60% real loss) in twenty years and yet to leave the buy to let rentiers trading in second-hand hopes, with their 60% real gain in that time, untouched.
And don’t give us the dividends argument; the buy to let plutocrats get plenty of rent and all their sticky little service charges. This measure simply hits the workers and investors in business and pampers the bureaucrats and the rentiers. It makes very little sense, unless you are a senior civil servant or a retired prime minister, like Blair, of course.
Chinese insularity - the new version
Meanwhile China I feel is now detaching itself from both the rule of international law (in so far as it ever bothered) and more interestingly the world financial system. It may indeed end up better off, but for now (and this is also a change from much of the last 50 years) it does not feel it needs to attract external capital.
So much of its trade and capital markets engagement has been predicated on securing capital; this is an odd and novel twist. Although perhaps a logical response to the West, who rather than conserving capital as a scare resource, are immersing the world in torrents of surplus cash and inflation.
Much of China’s policy about their own global investment (so outside China) also used to have the same theme, driven by the desire for returns, influence and to hold their own export-based currency down.
But no more, it seems, and their inherent desire for autarchy, the hermit kingdom trope, has only been emphasized by Trump, WHO and the madness of the internet. It apparently wants to be the new Germany, (no longer the new USA), so it will be insular and conservative: cautious, not driven mad by debt and the baubles it procures.
Well, if true it will be different, whether it can really be done, without a wave of disruptive defaults is unclear, but don’t doubt the length of vision, so unlike our own government. While a theme of this century has also been where China leads, the rest must reluctantly follow.
Even a dog has its day, but for investors both the UK and China now feel significantly more canine than at the start of the summer.
ALL QUIET: Covid and UK Property

A brief glance at an excellent first half for investors: thoroughly “risk on” for the first quarter, but a slower but still an upward grind thereafter. Not that such arbitrary dates matter. What does count is what can make it kick on from here?
Covid patterns
So, first a glance at COVID, or rather our reaction to it. The disease itself is now less important in most OECD economies, they have the capacity to deal with it, vile though it is, and the vaccine numbers are rising steadily, faster than we expected in the UK.

This is a screenshot from this website at Johns Hopkins University : https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
In raw demographic terms, in most places it is barely a flicker on the remorseless upward march of global population growth, but the extraordinary evasive action being taken mattered much more, and I see little sign of that abating.

Watch a dynamic map of all births and deaths at this site: https://srv1.worldometers.info/world-population/ (these figures include all deaths, not just from Covid 19.)
One of the key issues is that, for whatever reason, it is prone to sudden spikes, the only defence to which is almost complete (90%?) vaccine coverage. Indeed, the spikes can clearly ride quite widespread vaccination, higher than originally thought. But the spikes last weeks, perhaps a month, and for most of the year, most places are not experiencing them.
The trouble, especially in the UK, is our muddled policy response is to take down the economy on a semi-permanent basis, almost as a fetish against the lurking evil. To put in place colossal support measures for spikes that are transient is both cripplingly expensive and turns emergency response into embedded base cost. We are on a constant war footing, even when the enemy has seeped away to regroup.
So, despite Mr. Javid’s optimism, we do expect the bureaucracy to cling onto extensive controls, that limit capacity in public services and many consumer sectors. I had hoped that the ridiculous restrictions would bear down on the elite’s summer holidays, but I now understand they don’t care, as they clearly don’t obey them anyway.
HOW MUCH MORE DELAY CAN THIS 'REOPENING TRADE' TAKE?
Which brings us to two thoughts, firstly the re-opening trade is shrugging off some mighty setbacks, and very little of the run up from last November was based on controls extending into 2022.
At some point balance sheets will start to crack, and values will then retreat.
Commercial property sector
The other is a more sector specific concern, but also a straw in the wind, in the extension of the UK commercial eviction ban well into 2022. I don’t follow the logic of that, it is a significant ongoing seizure of private property rights, it is not clear to what end. It is not protecting jobs, unless furlough is also to be extended. It appears to assume businesses can occupy premises rent free for an extended time period, although the Government also suggests (slightly oddly) that much of their business support package (mainly loans, with government backing) can be used to pay rent.
Not that I care much for commercial landlords, who have long been over protected in the UK and exploitative, but it is to me, an odd move. We looked at real estate earlier in the year and expressed support for the TR Property Investment Trust in particular, in February, after which it has been on a run. But reading a quartet of March year end REIT annual accounts, I feel rather less sanguine: those are British Land, Land Securities, Helical and NewRiver.
The trouble here is they got hammered last year, with their March rent collections a mess, and double figure valuation drops on the retail side, they have been hammered again this year, with similar double figure write downs, and now it looks like they could be hammered for the current year too. That’s a lot of damage for the sector.
Office rents are holding up, collections are better, surrenders fewer, but they are running hard to stand still, with typical average lease lengths in single figures; this brings a lot of renewals too close for comfort. Time off debt maturities is also becoming significant.
Some Specifics on British Land, Land Securities, New River.
Equally clearly a lot of London occupiers, in particular, will have spare space, probably well into 2024 and maybe forever. Successive asset write downs, keep eating into the debt cushion, rates are low, so debt service is not an issue, but covenants are tightening, cash flow for development is getting squeezed and banks are not sitting back, just because the tenants have a state license not to pay.
They do differ of course, British Land is fairly serene, based on London offices. Land Securities having been boring for so long has appointed a new team, from the student accommodation and logistics worlds. Granted both were good performers in the last decade, but they are talking of ditching much of the existing portfolio, to chase development schemes. Brave if nothing else, one might say. Helical is smaller but goes for ultra-high quality office refurbishments and expansions, with tenants who can pay for quality, but each of their complex inner-city projects can take years to get through planning and their growth depends on a steady stream of them. After current ones complete, there will be a hiatus.
While NewRiver, always an aggressive high (and at times uncovered) yield stock, also looks strange. Debt is substantial, and another double figure fall in values could be harsh. Granted that would take more of its yields into double figure territory, in areas where demand (and alternative uses) should really provide a floor. But it also flirted with a badly timed foray into pubs, and their valuers are (to no great surprise) saying valuations for those are in the “who knows?” realm. Meanwhile the finance man is apparently jumping ship to lead a spin-off of the licensed premises, which sends some quite odd signals, although maybe holders have tired of his complex skills.
This leaves a more bifurcated market than ever, but with the risk of overvaluations both in the good stuff (last mile logistics in particular) and storage in general, and in residential.
By contrast UK retail is looking ever more wounded. It has been a great reopening trade, but unless the runway is really getting cleared, take off may now be too late for some.
Meanwhile Boris can’t seem to let go, having gained control, freedom is clearly an unattractive option to those in power. If that stays the same, we can see a perfect real estate storm brewing, if and when liquidity dries up a little.
The umbrella organisation, RICS, has in the mean time this summary to offer as its full market survey results.
Politics in the constituency of a murdered labour politician
Finally, the odd thing about Batley and Spen, was the idea that the Tories could win. I looked up the odds on Labour last week, at 4: 1 against, I found them most attractive. And that was based on my wrongly writing off Gorgeous George, who mercifully is one of a kind.
Without his strange allure it was and is very solidly Labour. Another non-story, I fear.
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd
A HARD RAIN
WHEN WILL MARKETS RESPOND?
Everything is in the end politics; it just takes a long route on occasion and rather like a frog in water, markets take time to realize that the pleasant feeling of warmth is a prelude to being boiled alive. We are well into the boiling phase, but how long before it all registers and an escape is finally attempted?
The purpose of politics seems ultimately to take an individual’s wealth and the fruits of their labour and give it firstly to the friends and allies of the confiscatory state and then use the remainder to buy votes. That bit does not ever really change, whoever is in charge.
So how does that truism impact markets on each side of the pond? Well, traditionally the UK state has been far greedier and done far more harm to the economy, than the US state has, which is why both GDP per capita is far worse than the US, and the FTSE has failed to rise, even in nominal terms, in two decades. Add back inflation and investing in UK PLC has been a long-term wealth destroyer. It enjoys that characteristic with the rest of Europe. As we have long said, lift the lid on any sensible UK pension fund, and you will find a lot of Apples inside.
In general, and this too is a platitude, well run dictatorships, especially those with access to world markets, do far better still, hence the rise of China. Of course, “well run” and “dictatorship” seldom sit well together, but nor do “populist” and “well run”. In general markets are not greatly in favour of either populists or dictators, feeling the rule of law is not something either care that much about. But by implication neither are voters now too fussed about laws either.
LONDON OR WALL STREET FOR THE REST OF 21? - THE BIGGER PICTURE
So, the investing question is whether the US, despite being increasingly under the control of the populist wing of the Democratic Party, is a better bet than the UK? Or do we have the capacity to process a bigger picture?

And of course, we need to ask whether China is better than both. So far, the US is finding Biden to be no worse than the populist wing of the Republican Party, and the UK is feeling rather baffled, given Boris constantly talks right but acts left.
Put like that our current sentiment, that Biden will cause more damage than Boris, is at the least contentious. So, we should look for the good in Boris and the bad in Biden, to help justify that call. Not an easy balance, but what makes it easier is the relative valuations. In particular of tech, where the US has moved ahead massively, so a lot of the question can almost be reduced to asking if Tesla is worth it? Or if it is, what is the motivating force to make it still more overpriced?
Boris seems to be trapped by the doctors and his inability to fathom numbers, into driving us into a permanent state of fear and welfare dependency, which will keep the UK steadily in long term decline. If he can break free of that populist vice, we might have a slim chance.
The omens are mixed, banning travel to Portugal (again) looks like the familiar science trap, but of course might be a reaction to the EU also banning wider travel from the UK to the EU just before that. Given our relations with the EU, that oddly seems more likely (if childish).
By contrast the US is now operating near normally, a stark contrast, as we remain in de facto lockdown, tied up in fiddly, unpredictable, illogical restrictions.
CULTURE WARS AS INDICATORS OF INVESTOR SENTIMENT
Both the Queen’s Speech setting out the legislative agenda for the year and the visit of Viktor Orban, the Hungarian premier, may have been light on substance (they were), but boy were they heavy with Tory symbolism, coming hard on the heels of the local election wins.
Much of that proposed legislation was to placate the grass roots, I seriously doubt laws on de-platforming (of both the living and the stone hewn) will make much difference, but the Conservative base feels it is high time the left got some mild resistance, in cultural matters. There has been very little of that for the last two decades.
I suppose the brutal bashing of Bashir is in the same category, although from my own experience a BBC journalist who did not lie and cheat their way to a non-existent story, would have been the truer rarity. Although in that they differ little from the rest of their breed, but defenestrations at the National Gallery and revolt at the National Trust, have been a long time coming and indicate a new degree of solidity and confidence. This is long overdue since Blair assiduously stuffed placemen into those organisations. Neither Cameron nor May did much about them, having their focus on higher things, it transpires.
Does it matter? Well not really, to markets, but it is a counter to the reckless spending, and the chilling clarity with which Boris famously expressed his view on business during Brexit, so is a straw in the wind. Maybe other things will change.
DEFUND THE DOLLAR?
What of Biden, well so far the US markets have taken slow comfort from the slender political majority, he holds, but the view is creeping in, that he really is going for broke, he is happy to unleash inflation, almost keen to do so, that letting Wall Street blow itself up, in the meme stock nonsense, and suppressing interest rates (which is vital if you are borrowing so much) and as a result trashing the dollar, is all fine, all part of the plan. Note the recent measures by China to prevent their currency appreciating too fast and by Putin (of all people) complaining at dollar fragility. Others may not attack it yet, but it increasingly looks like US policy.
Much of that perhaps matters little to Wall Street immediately; inflation makes you own real assets, bonds are now utter rubbish and so far, very little of US individual wealth is invested abroad. So, Wall Street almost inevitably drives itself up and that’s a hard tiger to dismount.
But it maybe matters more to us Europeans, who need to both believe that US overvaluations will persist and critically that the dollar will not weaken further.

So, in the end politics do matter, not now, not today, but how these contrasting styles evolve over the rest of the year, will be very important to how currencies and markets respond.
Getting it right for the second half involves a big call, this year, as it did last.
Flat markets are not always still markets.
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd
06.06.21
YELLOW BRICK ROAD
The recent elections in the UK probably result in a mildly stronger position for Boris in his Merkel persona, his Christian Democrat (CDU) disguise, so the fiscally left wing, culturally right-wing hybrid, that seems popular; but other than disasters averted, the poll achieves little more. For all the noise about the Hartlepool by-election, we are talking very small numbers, with a 40% turnout in a seat already slightly subscale due to depopulation and industrial decline. It has no resulting impact on the governing majority. Indeed, but for the Brexit Party, it would have been Tory already, so it really says nothing about the right-wing vote. The Tory Party is still miles from representing a majority view, but as long as the left is divided and the right united, that will persist.
Nor do I see much of interest in the council elections: a good result for the Tories in building on an already strong performance last time, which shifts the middle third of councils around in the quagmires of NOC or No Overall Control. This morass, like the bilges on a boat, washes left or right depending on the political tide. But with staff (and councillors) aware that only a few seats can shift them in or out of the NOC swamp, its impact is not great, particularly where they have elections three years out of four. These permanently transient councils tend to be run more for themselves than anything tedious like ideology or providing decent local services.
Neither Mayors nor Police Commissioners have any major power. Sadiq Khan, freshly back in office, faces a central government happy to call in his local plan (on housing) and impose central government representatives on his transport authority, thereby strapping one hand behind his back, in both his areas of real influence. Meanwhile London policing remains ultimately under Home Office control, so like the other areas is just for political grandstanding, not real service delivery. Policing in London also seems an enduring disaster: where it is needed, it is not wanted, where it is wanted, it is not needed.
Reading the Party Runes
So, what of Kier Starmer? Well, it also tells us little about his Cameron-lite policy of avoiding controversy, avoiding spending on fights he can neither win nor cares about, and ensuring he controls everything in the party. That policy is seemingly intact. The Corbyn wing will continue to spout for the microphones on demand, but matter little. The key issue is whether the big funders will want to have a go at winning the 2024 election. I think they will, but should they decide it too is lost, Starmer has a problem. If the party’s money bags decide he can’t win, he won’t.
For Boris it is at the least an endorsement of his recent COVID strategy, and that higher taxation to pay for the incredible spending splurge, has yet to impinge on voters’ minds. So, it permits him to carry on, but perhaps recover more of a strategic view, after the recent wallpaper storms? Does it make exiting COVID lockdowns any easier? Well, it should, but hard to tell if it will. Does it validate the extreme turn green? Not really, the Greens still did better in terms of new seats won, than either the Labour or Lib Dems, and are still advancing (from a very low base).
I am not sure if the Lib Dems expected much, they have Keir’s problem of irrelevance tied to being pro-European, when the EU is behaving more oddly than ever. So roughly holding their ground was fine. Indeed, they polled way ahead (17%) of national election ratings (which are more like 7%), but not over the magic 20% required to hit much power.
Those Strange US Job Numbers
Which brings us to the real shock from last week, the weird US jobs numbers on Friday. We have long said that how and if labour markets clear after the great lockdown experiment, is the vital economic issue. The problem never was the banks (so last crisis) nor the ability to borrow to sling money down the giant hole dug by the virus. Both are easy. But once you have smashed the economic system, does it regrow, like a lizard’s tail or simply start to rot and decay?
Many of us would have avoided the deep wound in the first place, but now the experiment has been started it must conclude. So, what did happen to slash monthly US job creation from expectations of a million to just a quarter of that? The instant reaction that it meant inflation has gone and so bonds were fine, was as instant reactions often are, garbage.
The bull or ‘Biden’ case is that as they have the right medicine, it just needs a bigger dose, or to take it for longer. Seems credible; labour force stats are notoriously volatile, some of the job losses came from manufacturing, where supply shortages are biting, but that’s transient. Some seem to indicate a mismatch of jobs to vacancies, hopefully also transitory.
Encouragingly, a spike in wage inflation and hourly rates indicated plenty of demand for workers.
Yet, slamming the brakes on, shutting the economy down and paying millions of people not to work, might have brutally destroyed the delicate economic system. Thousands of small firms, where the bulk of employment is created, have just gone. The complex prior system of sales, working capital, scheduling, delivering, inventory, payment has been eliminated. Sure, the people still exist, so do the premises, but the invisible mass, the self-directing hive, is lost: no map, no honey, no queen.

Bigger firms are also planning to work differently, perhaps needing less labour.
Once you stop working and get paid to be idle, and indeed have limited ways to spend your money, it feels easier to stay in bed, study Python, redecorate the house, or whatever, but not get back on the treadmill. Indeed, in a lot of cases, once you step off, stepping back on is hard and also downright counter intuitive. Sure, your old boss wants you back, but do you want the old boss back? Worth a look round at least? As the title song puts it, “there’s plenty like me to be found”.
Well, we still go with the bull case.
However, the bear one is not trivial. If you can’t get labour markets to clear, welfare will be embedded, as will high unemployment, deficits and unrest. It remains the most critical feature, worldwide of the recovery, and several questions about it remain as well, including the need to keep new bank lending elevated, cheap, available. Expanding needs cash, contracting creates it.
The oddity to us then remains, that if the liquidity barrage really does work, why should it work better in the US than elsewhere?
And if it works the same for all, don’t US markets then look rather expensive?
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd
What doesn’t sink me makes me stronger
First published on 20 December 2020

A strange old year winds down, with proof once more of the exceptional power of suggestion and the great strength of cohesion.
Tired Markets, Bullish Investors
So what now? Clearly markets are tired, we have the odd position that investors are almost universally bullish on next year, that fund managers report unusually low uninvested cash, and yet it still feels like there’s no great power behind the mainstream markets. Indeed, over much of the developed world after the November vaccine/Biden sudden jump in markets, not that much has happened overall, a slow grind higher at best.
We see that lull as temporary, reflecting the month or so of pain and uncertainty before the onset of spring. Yet if anything we ourselves also want a little more liquidity, driven in part, by our awareness that markets are always thin and unstable going into the year end, so we can see little to be gained by jumping in this week.
Typically positions for 2021 will be taken in mid-January, once we have a reasonable steer on how 2020 ended. Not that that matters greatly either, neither of the next two quarters (or indeed the last two) will be in any way normal, Q1 2021 will be heavily influenced by COVID, but 2021 Q2 will see it fade very fast in the sunlight. Lots of scope for extreme volatility in that switch around.
But then, why rush in?
A lot could still go wrong. We assume Brexit disputes are just typical posturing for the crowd, but given those involved, maybe that’s brave. We assume the vaccines will work, which is one of the key points in this whole saga. Indeed, almost everything has been conjecture and spin, with the virus seeming to come and go regardless of our frantic efforts and illusions. It has been barely possible to discern cause and effect for all our demented jumping about. However, the vaccine is going to be at last a single, vital, fixed data point.
By late January if we (and the markets) are right, the most vulnerable will have been given a 95% effective shot, excess mortality should tumble, indeed you should almost be able to watch the vaccine defences build week by week, as ICU’s empty. The rush to start vaccination, played far better by the UK (a rare event it is true) was all about getting the vulnerable sheltered before the very worst of the winter. In that case this epidemic is over, and the fearsome fangs will have been drawn in a few weeks.
So, in that case, why dive in now, if waiting a short while answers that most fundamental question. Besides nearly everything looks too good to be true. Our own returns are clearly too good, typically they have been double figures for most managers, even our low volatility products are (depending of course on the next week) going to end up there, which is truly exceptional for a good year. For a year in which economic growth has been halted for so much of the time, it is downright amazing.
Overbought?
We have already (in the VT-GTRF) shifted into slightly higher risk areas, such as Listed Private Equity, where we see good value. But we are reluctant to go much deeper just yet. Every emerging market that feels half credible is already at a twelve month high, and frankly the data from those is even less reliable than ours. All the Wall Street overbought signals are flashing red. There is clearly too much speculative cash racing about looking for a home, be it DoorDash or those irrepressible SPACs.
Government debt is in an elegant swallow dive onto the zero axis, you are getting very little return to lend to some odd places.
So, we will enjoy some pensive digestion after the feast, if we are somehow wrong to the upside, we almost don’t care, what’s better than best? Being wrong to the downside, seems the graver error.
Echoes of the Weimar
We started with a quote from one of the trio of great Weimar philosophers; now there is a history to conjure with. In a year when democracy seemed set to topple, when there are indeed no facts only interpretations and when it became government policy globally to stoke up inflation to destroy the value of money and create negative interest rates, Weimar has many echoes. Throwing in its capture by a communist dictatorship and assault by ideological zealots, leading to near terminal decline, means comparisons just get too spooky.
So, to leave you with one of the Weimar trio, as you head into whatever glee Boris has left with you, “Man muss noch Chaos in sich haben, um einen tanzenden Stern gebaren zu konnen”.
That is, we all need, in whatever we do, a bit of luck, inspiration or indeed plain chaos to pick up the inspiration to move on to better things.
We wish you well for Christmas and the New Year.
We will return to the fray on the 10th January, no wiser, but we will hopefully know more.
Charles Gillams