Three big topics this week from three central banks, all of whom look to be in a muddle, with their knitting all jumbled up and highly implausible. Entirely predictable inflation meanwhile threatens to sweep them off their path, as they tinker with micro adjustments to interest rates.
Boris is diverting, but we doubt if it all matters; pre-Christmas entertainment. If he were logical or even vaguely numerate, he would change, but he’s not, and he won’t, but nor does he need to.
The Lib Dems win a by-election, that Labour fails to contest, but it makes no difference in Parliament, and it lets Boris look contrite mid-term. He will survive this with ease.
Which is not to say he should, or that he’s not making a hash of COVID, the sequel. In keeping the NHS in its current format, Boris fails to ask, as many have before him, whether it is still fit for purpose. This remains an urgent question. It can’t simply collapse every year.
Bailey – Bank Governor and historian
But perhaps Andrew Bailey, Governor of the Bank of England, understands the extraordinary risks Boris poses to the economy, and has hiked rates to show that. A Cambridge (Queens) historian, with a doctorate on the impact of the Napoleonic Wars on the cotton industry of Lancashire, he will know full well the impact of a French orchestrated trade war backed up by a dodgy pan European monetary system.
A consummate insider, via the LSE, he moved on to the ascending ladder of the Bank, which did include a slightly unfortunate move into the FCA. This turned out to have rather more real villains than he was used to. Married to the head of the Department of Government at the LSE, he will be very well aware of the political game and the current mood in Whitehall.
He’s seen enough inflation and has decided the Bank must pretend to act. Not only is the rate rise trivial, but it also coincides with a continuation of Government bond buying (QE), an odd call. That the last thing the economy needed was still more liquidity, has surely been obvious for eighteen months now.
Christine Lagarde and Jerome Powell
In Europe the same mishmash exists. We have been hearing Christine Lagarde explain why the ECB is now accelerating one asset buy back (APP) while ending another one (PEPP). She was winging it with the phrase “utterly clear” in answer to a pertinent question, when it was clearly anything but. Still, she did seem to have her ear rather closer to the ground on wage inflation, at least compared to Jerome Powell.
He by contrast has been caught with his pants on fire, trying to weasel his way out of the Fed failing to spot inflation, by saying that most market commentators agreed. Remind me, which is the canine, and which the wagging appendage?
Basic economics – why inflation arises
We called it on inflation as soon as that stock market rally took off, and for the simplest of economic reasons: the pandemic had reduced global productive capacity, so absent a change in price levels, the economy was less productive, profits were therefore lower, competition would therefore be less (unless prices rose), and total production must fall. Less output, same demand will always mean inflation.
Forget the energy issue, forget supply chains, less capacity, more demand always means trouble. True based on that one schoolboy error, the dopey measures to reduce capacity further by more regulation, hiking the minimum wage, paying people not to work and so on, plus embarking on accelerated decarbonization and a few new trade wars, was not going to help much either. But please no more “surprise” inflation, it was baked in. (See extract from my book, Smoke on the Water, blog dated July 2020, title re-appearing shortly on Amazon)
After the interest rate rise
However, we have also long felt that interest rates can’t rise enough to stop inflation, but that as governments have to back off fiscal stimulus, as they are already overborrowed, the lower productive capacity will itself shrink demand, and in the end cause inflation to fall. But we see that as taking years, not months.
Why are interest rates not rising to combat inflation? No political will for a start, and any one country that gets too far out of line will find currency appreciation itself addresses the problem. So, do we believe the US “dot plot” suggesting three rate rises in 2022, while the Euro zone does nothing? We struggle to.
Powell is still clinging to the lower workforce participation rate (which matters) as a signal to defer rate rises and not the unemployment rate (which is more closely related to vacancies) and hence of less fundamental relevance. While employment is great, it will still be unattractive if inflation (and fiscal drag) takes off, thereby holding the participation rate low.
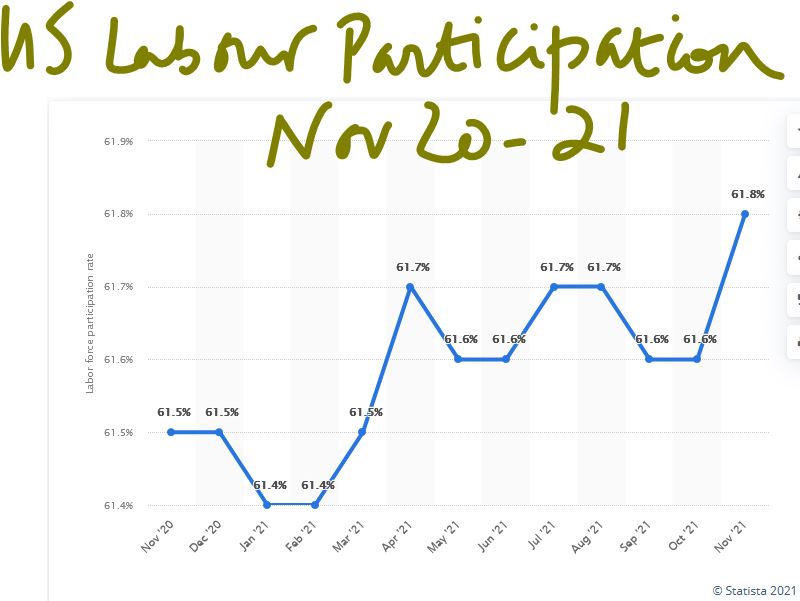
This does still suggest dollar strength, while sterling like other smaller currencies always needs to be wary of getting too far out of line with US rates. But also, a need to fathom out the new look economy. To us, it does not seem service industries that rely on cheap labour are operating in the same world they grew up in. Certainly not if it is onshore.
There is a forced change in government consumption patterns (and hence employment), and this will also be telling. We are heading into quite a different market, when all this shakes down.
Sitting on high cash levels over Christmas, as we are, is pretty cowardly, but if you can’t see the way ahead, slow speeds are usually safer.
We do also rather agree with Chico Marx, this year at least.
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd