The name of the game
What is the point of investing? How has that changed over time.? Do we still need so many choices? Are single stocks relevant? And we salute the prime palindrome.
We were taught that investing is an economic process for allocating capital to allow competition to seek out the best opportunities and fund the best businesses for the benefit of all. Countries with good markets have good capital allocation, grow faster as enterprises with the best return on capital, and then attract more of it.
Really? Not what it looks like now. Things change. The old gateways got knocked down, so anyone can access any investment anywhere. The paternalistic City was never sure about that, but in reality, markets followed communications, which went global.
The FCA (and to a degree the SEC) has a muscle memory of these protected times, and constantly wants to suppress innovation, keep new issues and ideas away from investors. Slow it all down, so they don’t just regulate markets, but control them. But excess capital flows are changing all that. It is instructive how the SEC, by trying to stop Bitcoin, has simply made it respectable and transacting in it safe.
And looking skyward and not understanding how this excess liquidity is created by quantitative easing is sadly no longer viable for investors; entire economies are built on it, like Japan. Nor is it transitory, it is embedded in the US and EU as much as anywhere.
Governments hoped to take control, using QE they forced the cost, to them, of debt down to zero, on the way creating such a shortage of bonds, that prices rocketed. Paradoxically as did equities, for they could keep offering a yield and had no “lower bound”, so their prices could rise for ever.
Then equity investors got back in control, they realised they could move the price, on the thin sliver of equities that are actually traded, pretty much as they wished. In particular they could signal or co-ordinate, so that everyone was on board with the price direction. Which is both the meme stock phenomenon, but also at the heart of momentum investment.
And liquid, global, interconnected exchanges were designed to let all those price signals out in an instant. Of course, co-ordinating them takes only a few seconds more.
THE POINT IS
Which brings us back to what the point of investing is. I am only interested in capital allocation, if by understanding it and dissecting the choices, I can get better returns.
I can have an altruistic angle of course, I just like old style engineering and banking outfits, I sponsored the IPO of an art gallery once. I have a soft spot for Kenya and Bulgaria. I want to avoid ‘defence’ industries, I dislike tobacco and polluters, and not sold on slave labour either. How nice, and in the investing world, how utterly useless. Never, ever, fall in love with a stock they said: quite right, sadly.
Indeed, what you and I call capital allocation is what others call hot money, and it moves faster and faster. As for those bad actors, well money always attracts crime, the faster it moves the more options for criminals exist, quite a few of whom wear suits.
But then who needs stocks and analysis when you can now buy a market cheaply? Everything says invest in multiple geographies, but really? The process I have outlined above favours one or two markets, they win, so they give a good capital return, so they win again, almost regardless of what the underlying business does.
Indeed, Bitcoin shows, it can indeed be regardless of the underlying asset. Coordination and belief matter, not reality.
So, what of all the rest, the unfashionable markets, unfashionable stocks, they just keep underperforming, keep being sold, with very little scope to recover. With rates low it was possible to pay a competitive dividend, but when money market funds are expected to offer you twice the rate of inflation, even those dividends are unattractive, and they get taxed hard.
NO COMPETITION IN COMPETITION
While the Government has also destroyed the competitive market for companies, by largely sidelining hostile takeover bids. In any event issuing poorly rated paper for poorly rated paper never sounds great. But that closes out profitable exits; sure you get insiders sweeping the Aim floor for cheap deals, but by definition those are not competitive, you can’t have two sides both inside.
The government knows that almost any deal has a loser, or someone not as well protected for life, as they had hoped. Which means media noise and MP’s getting lobbied, so far better to ‘long grass’ it, via a competition investigation. Isn’t it odd that the competitive market in asset allocation created by an active takeover market, is the one market the competition authorities simply won’t investigate. But without that cheap stocks just stay cheap, it is why buy backs are so prevalent: the companies are right, the price is wrong.
Of course, index investing has issues, you buy the bomb maker, cigarette seller and dodgy legal firm all in one bundle, but that’s the game. If it is big enough, it goes in the index, and you buy the package.
And hot stocks are likely to favour low commission markets, and low transaction costs. It may be an accident, that UK commission and tax is based on total deal value, but US commission is based on share count (and there is no stamp tax). But it does mean that you buy a share in Berkshire Hathaway for the same dealing cost as one in Game Stop, or if you prefer Nvidia and Trump Media.
Assuming sanity, you trade in the US, or in stamp free index ETF’s, not UK stocks. Although the FCA are fighting a rearguard action against both ideas, with the discrimination against holding ETFs seeming particularly bone headed and indeed against consumer interests.
But few stocks, fewer markets, more hot stock volatility, it is just the way we have set it up, don’t be surprised that is how capital is now allocated, growth funded, prosperity achieved and destroyed.
TIME FOR A BREAK
As for this market, it had to break, we have said it for a while.
Levels have dropped sharply, and money is rotating back into bonds, or at least not flowing out of bonds.
Waiting to see through the summer, when that first rate cut arrives and who wins the US Presidential election, is all impacting the hot flows and making staying in cash feel easier.
While a more sinister undertow is coming from the narrative that the terminal interest rate settles out higher.
Our core assumption is still that real interest rates are now in a steady decline, but the equity bonanza of negative real rates is not coming back anytime soon. While for now, only one Central Bank and one market is going to keep on winning the hot money race. No prizes for second anymore.
The Winner Takes It All.
Jerome K Wiley?
We do think Powell is running off a cliff, just not the one the market assumes. As we endured the wettest February since (at least) 1836, when William Lamb was prime minister, and the wettest Tory government since records began, is there any chance of dryer times?
But first the tiresome tango of rate rises, the market swept to and fro, nation by nation, until the firm stamp of a well-heeled bond whips the whole mass back round again.
Bailey of the BoE, and Powell of the Fed
So, this week it is to be Bailey first out the gate, FTSE up, bond yields down, next week who knows? That rates will fall this year is the only certainty and the big US markets have built a near vertical climb out of that snippet. But you will note, not in rate sensitive stocks, the Russell (small cap) is still pretty flat, weighed down by the regional banks that dominate it.
And Powell, he’s guessing or as he calls it is “data dependent”, but for all that he is pretty happy projecting those guesses forward. So, he has moved from three rate cuts this year, to a new position of ? Well - three rate cuts this year. Not much data dependency there.
Before long he will run out of “this year”, because the inflation numbers are not behaving, nor critically is the oil price. Like Bailey in the UK, he is desperate to cut and under heavy political pressure to do so, both have said 2% inflation is not now needed, just moves in the right direction.
I feel the only thing that can get us there is a sudden (and indeed overdue) drop in the energy price, which we do expect in the summer, but who knows? It has held up rather well so far.
So, at the moment, Powell is perhaps running on thin air. Protectionism and vote buying fiscal measures mean he can’t get there without some other help.
Markets are supercharged – is it sustainable though?
And if rate cuts are what has supercharged markets in the US, I don’t see that as sustainable right through the year. It might instead be the possibility of a more market friendly, fiscally prudent, Trump, which would be more logical, in some ways; but that still feels implausible.
Nor do I see, as yet, many other markets joining in. Partly, why own anything else but the NASDAQ? Some markets have moved (Germany, Japan) but you could also argue that was after being oversold for too long. While the Swiss have cut rates, it is in part (as ever) to restrain their currency, I am less sure others will want to move ahead of the US.
They may be forced to, but there again their scope before European and UK elections looks limited. And some parts of the market, like UK smaller companies and many REITs (and some renewables) are not signalling anything but yet more damage and destruction, from suspect refinancing at high rates and over optimism on revenue.
Air Cushions
It was notable too how keen Powell is to slow the tightening imposed by reducing the Federal Reserve bond holdings, which has to date been done at a fairly brisk pace. He now talks of stabilising holdings, (in other words resuming bond buying, stopping the runoff of expired holdings) at what seems a high level, for fear of taking too much liquidity out of the system.
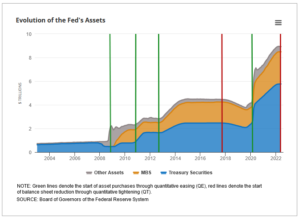
From this explanatory article on the process by the Richmond Fed.
For a while rates and reserve sales were working as one against inflation, but not for much longer it seems. Which should be good for bitcoin and other liquidity consuming monsters, if nothing else.
Who is Next in the UK?
The interesting Tory battle is between the Official wing, now entrenched in power, and showing no sign of intelligent life, beyond wanting to “make a good fist of it” in the inevitable electoral defeat. Then there is the Rebel wing, keen to cause trouble, break things, get popular support, or be nasty, if it gets them attention. Although the Official wing regards this as disloyal, it follows an old pattern. It is not just about this particular bunch: see this paper.
Faced with a like quandary under Blair, the Tory party swung left, towards the centre and power, just as Gordon Brown started the decade long Labour march to irrelevance. The Official assumption is that will work again, although the alternative scenario is that Starmer settles down in the centre for the long haul, and the Rebel wing, kept securely away from power, withers for lack of a structure.
But all ruling parties were, by definition, rebels once.
Back in 1836, William Lamb was an unsuccessful politician, wrapped around by Peel, sent to the House of Lords, then brought back as a centrist Prime Minister, and being generally useless, was turfed out again, after naming an Australian city, en route. One must hope for no repeats from history.

William Lamb, Lord Melbourne – from this site
It does not feel time for compromise candidates, nor will a ‘safe pair of hands’ do. Rishi is in a fight.
Meanwhile the fields here feel like salt marshes, dark water lurking in deep cracks, the lips of which slide into clay and suck at the soles of your feet. We certainly could do with some heat.
I do expect this run in markets to go on, but the upside in the big US indices looks more limited and broader participation elsewhere will await those rate cuts. Both their size and speed have a capacity to disappoint, especially when they are so hotly anticipated.
The politics, a long time coming, may become more influential. It could get choppy.
We will take an Easter break, after what feels like a long spring.
And return with the sun (we hope) on 14th April.
By their works . . .
Well, the works this week: a pensive Jerome Powell does nothing, a reckless Andrew Bailey does nothing, Canada joins Biden in picking fights, and the bulk of most equity markets are stuck, going nowhere.
NO MORE US RISES
So, the apparently knowledgeable financial press said that Powell predicts rate rises? He said nothing of the sort of course. True the other members of the FOMC dot plots were in aggregate higher than the current rate, but by a fraction, it is like the average family being 2.4 children, meaning everyone, in the absence of King Solomon, has three children. No, it does not, it means on average there are no more rate rises.
So, Powell has stopped the runaway train, by lighting red flares in front of it and throwing railway sleepers across the track. Job done. Inflation is way below base rates. Bailey has asked nicely and tried to lasso the inflation express from half a mile down the track - won’t work. Inflation above base rates is misery, inflation below base rates is time to loosen.
Powell did start rambling, describing parts of the economy with “by their works ye shall know them” but decided that was all a bit erudite, before he had even finished the thought. He then reverted to the old saw, “forecasters are a humble lot, (with much to be humble about)”. Presumably that is unlike Central Bankers? I still think that judging them by their works makes sense.
But Powell is happy: the Q&A session threw him a litany of gloom, government shut down, students having to repay debt, auto plant shut downs, but no, all is fine.
The core US consumer and therefore the US economy, is in a good place was his verdict.
BAILEY DITHERS
Bailey seems to like to crash the pound every October, which is not good for inflation, just as picking fights globally is not good for oil prices. And it is also bad for inflation.
And either the UK government will cave in to public sector strikes or productivity will keep falling due to said strikes. Neither are much good for the economy. Nor is it good for the markets: in performance terms, the UK remains the sick man of Europe, amongst major markets.
THE MAGNIFICENT SEVEN RIDE ON
I was at the annual Quality Growth conference in London again, a stock picker’s feast as usual. It seems that if enough stock pickers can agree on the menu, as the dominant prevailing theory of investments, they will drive the prices of their favoured stocks ever higher. Which they do, it seems. This is helped by the ‘over the long run valuations don’t matter’ line, pushed hard by Baillie Gifford (amongst others). You might recall my article on Scottish Mortgage a while back.
And of course, as we know from both index and momentum investing, once something starts to move in a flat market, it keeps moving.
But that leaves the vast bulk of quoted stocks flat or down on the year, which makes some sense. When rates rise, bonds are substituted for stocks. The last two quarters in particular have been flat to soft, and while some of these stocks may have hit a bottom, it is still very hard to tell.
The only good news for UK investors is that Andrew Bailey has ensured their overseas (especially US) stocks have a nice currency tailwind.
MADE IN JAPAN
Meanwhile from Comgest there’s a radically different view of Japan. The equity rally there has been fantastic, but it is not the typical exporter boom of a weak yen, in their view, but more about bank stocks soaring on the expectation of the end of Central Bank rate control. This allows their vast balance sheets to earn a real return, at last. This is quite a departure from the general explanations about “this is Japan’s time”. That one has caught me out far too often, but explains the horror show from respected funds like Baillie Gifford Shin Nippon - small and illiquid is just nasty everywhere.
So, although the global rally looks to be strong, it is terribly narrow, and built on different foundations in different places. Or more positively, a broad advance awaits the first rate cuts, either from triumph (US) having controlled inflation or disaster (Europe) having created a recession and left inflation out of control. Either route to rate cuts wins, it seems.
GLASSHOUSES AND THROWING STONES
Oddly, I feel the Canadian spat with India is really quite serious, the tendency of rich Northern countries to preach, in this case standing very carefully behind the only global superpower’s shoulder, really annoys the global South. It has been going on for centuries and is at heart simply the old colonial mindset.
India’s continuing reaction may well portray the accuracy (or otherwise) of the allegations, as on the face of it this is deeply insulting to the world’s largest country, and one that has tiptoed down the line between offending the West and creating starvation and destitution for millions in the South.
I don’t believe it - murdering virtuous plumbers in Canada over the Punjab, which has long ceased to be a primary source of domestic concern, is plain weird.
All things are possible, and India cares far more about Kashmiri terrorism (for instance), but if it is false, expect a sizable slap to Canadian interests, and more accommodation for Putin.
After all, if you are treated as if you are behaving like Putin, why would you ostracize him?
Reserve in Reverse
Fallen Emperor?
With almost two thirds of global equity markets represented by the US, the fall in the dollar so far this year is quite dramatic, and for many investments, more important than the underlying asset.
UK retail investors are especially exposed to this, as although Jeremy Hunt (UK Chancellor) may not notice it, the US is where most UK investors went, when his party’s policies ensured the twenty-year stagnation in UK equity prices.
While Sunak continues to pump up wage inflation, which he claims, “won’t cause inflation, raise taxes or increase borrowings” Has he ever sounded more transparently daft? Sterling, knowing bare faced lies well enough, then simply drifts higher. Markets know such folly in wage negotiation can only lead to inflation and higher interest rates.
We noted back in the spring, in our reference to “dollar danger” that this trade (sell dollar, buy sterling) had started to matter, and we began looking for those hedged options, and to reduce dollar exposure. To a degree this turned out to be the right call, but in reality, the rate of climb of the NASDAQ, far exceeded the rate of the fall in the dollar.
While sadly the other way round, a lot of resource and energy positions fell because of weaker demand and the extra supply and stockpile drawdowns, which high prices will always produce. But that decline was then amplified by the falling dollar, as most commodities are priced in dollars. So, a lot of ‘safe’ havens (with high yields) turn out to have been unsafe again.
The impact of currency on inflation
Currency also has inflation impacts. Traditionally if the pound strengthens by 20%, then UK input prices fall 20%. The latest twelve-month range is from USD1.03 to USD1.31 now, a 28% rise in sterling.
In a lot of the inflation data, this is amplified by a similar 30% fall in energy, from $116 to $74 a barrel for crude over a year. In short, a massive reversal in the double price shock of last year. In fairness this is what Sunak had been banking on, and why the ‘greedflation’ meme is able to spread. But while that effect is indeed there, other policy errors clearly override and mask it.
A Barrier to the Fed.
In the US we expect the converse, rising inflation from the falling currency, maybe that is creeping through, but not identified as such, just yet, as price falls from supply chains clearing lead the way, but it is in there.
Finally, of course, this time, the dire performance of the FTSE is probably related to the same FX effect on overseas earnings assumptions. Plus, the odd mix of forecast data and historic numbers that we see increasingly and idiosyncratically used just in the UK. If the banks forecast a recession, regardless of that recession’s absence, they will raise loan loss reserves, and cut profits, even if the reserves never get used.
Meanwhile, UK property companies are now doing the same, valuing collapsing asset values on the basis of the expected recession, and not on actual trades. So, if you have an index with heavy exposures to stocks, that half look back, half reflect forward fears, it will usually be cheaper than the one based on reality.
Why so Insipid?
OK, so why is the dollar weak? Well, if we knew that, we would be FX traders. But funk and the Fed’s ‘front foot’ posture are the best answers we have, and both seem likely to be transient too.
If the world is saying don’t buy dollars, either from fear of the pandemic or Russian tank attacks or bank failures, that’s the funk. As confidence resumes and US equity valuations look more grotesque, the sheep venture further up the hill and out to sea. To buy in Europe or Japan, they must sell dollars.
The VIX, in case you were not watching, has Smaug like, resumed its long-tailed slumber, amidst a pile of lucre.
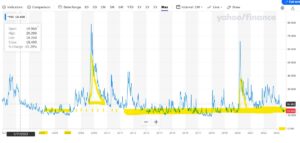
From Yahoo Finance CBOE Volatility Index
So as the four horsemen head back to the stables, the dollar suffers a loss.
The Fed was also into inflation fighting early; it revived the moribund bond markets, enticed European savers with positive nominal rates, (a pretty low-down trick, to grab market share) and announced the end of collective regal garment denial policies. But having started and then had muscular policies, it must end sooner, and perhaps at a lower level. So that too leads to a sell off in the dollar.
Where do we go instead?
So where do investors go instead?
In general, it is either to corporate debt, or other sovereigns. Japan is not playing, the Euro maybe fun, but not so much if Germany is getting back to normal sanity and balancing the books again. So, the cluster of highly indebted Western European issuers are next.
Sterling now ticks those boxes, plenty of debt, liquid market, no fear of rate cuts for a while, irresponsible borrowing, what is not to like?
For How Long
When does that end? Well, the funk has ended. You can see how the SVB failure caused a dip in the spring, but now the curve looks upward again. Although fear can come back at any time, as could some good news for the UK on inflation. However even the sharp drop the energy/exchange rate effects will cause soon, leave UK base rates well south of UK inflation rates.
So, every bit of good news for the Fed, is bad news if you hold US stocks here.
How high and how fast does sterling go?
Well, it has a bit of a tailwind, moves like any other market in fits and starts, but could well go a bit more in our view. Oddly the FTSE would be a hedge (of sorts).
A RIGHT OLD TONKIN
About Influence – American and Russian, mediated by the Chinese
So, to start with what does worry us: That is the slide to a hot war with the powerful Eastern autocracies, fueled by the EU with Napoleonic tendencies, an old man in the White House and a curious sense of ‘crusades’ with no consequences.
For those with long memories of American imperialism, the latest drama even fits neatly as a modern Gulf of Tonkin, a key moment in the slide to war. In that case (south of Hanoi) the clash was naval not aerial but was still notable as one directly between the warring parties and not just their local proxies.
While elsewhere the pieces move, China can not let Russia fail, nor descend into chaos, their long-shared border must stay intact and secure. They no more want the US there than the Russians do. The first step after his confirmation as ruler for life, by Xi, was indeed to go to Moscow.
And the bitter battles in the Middle East of Persian against Arab, Sunni against Shia have cooled abruptly, under Chinese influence. The world once more understands that the US is the threat to peace and stability, not just their fractious neighbours.
For Biden it is an easy fight, the Pentagon so far has played a blinder, what can go wrong? While, for now, France is Europe, no other large state has anything like their stability, Italy is led by the unspeakable, Germany has free market liberals in a bizarre ruling alliance with Greens, Spain is wrapped in its own forthcoming general election, the UK both distinctly detached and under a caretaker government.
The UK budget said nothing, incidentally.
Main influences in France.

While the left in France, as the above photograph shows, are very alive to Macron’s ambitions, to add more territory to the EU, arrange more protectionism for French goods and to suck the labour force out of adjacent states to serve the Inner Empire. Just like Bonaparte tried (and failed) to do, with dire consequences for the French nation.
For all that, the domestic fracas in France (which makes our own strikes look rather tame) was inevitable. Raising (by not a lot) the pension age from 62 to 64, against our own 67 looks small, but it was a clear campaign pledge.
The absence of any minor party wishing to self-destruct, by supporting it in the French legislature, is no great surprise either. So, he has implemented it by decree and Macron has dared the opposition to now either remove his prime ministerial nominee, or shut up.
Banking On Nothing
So, what of markets? Well, the end of SVB is no great loss, it had several policies that had to implode if rates rose, especially on the lending side. It was painfully ‘woke’; I can tell you more about the Board Members sexual orientation, gender and ethnicity than their banking experience, the former just creeps into the end of their latest Annual Report, the latter was invisible to me.
SVB’s long list of ESG triumphs and poses (and it is long) at no point included not going bust. It did commit an extra $5billion to climate change lending, which I guess has all gone up in smoke now. Still apart from all being fired, the bank insolvent, the remnants rescued by the hated Washington mob, under investigation by the DoJ, all the rest of their “G” was superb, and so, so, cool.
I don’t see Credit Suisse as a danger, although it may be in danger. It has had an appalling run of misfortunes, with musical chairs at the top, but it remains a cornerstone of Swiss identity. To let it fold would be highly damaging and cause shockwaves in derivatives markets.
Influence on the markets
So, I do understand the Friday sell off (who wants to be weekend long with regulators on the loose). And we do understand markets needed to go down, after the big October bounce, indeed it was a key reason for our building up over 33% cash or near cash at the previous month end. We knew the winter rally was fake.
But I don’t see this as much more. Retest of the S&P 500 October low? It should not be. I take a lot of heart from bitcoin soaring (63% YTD); if liquidity was short, that would not have happened.
But for all that, I don’t like March in financial markets, too much is uncertain. So, this is more a time for cautious adding, rather than hard buying, but if we get to Easter (and hoping to be wrong on the Tonkin analogy) it does seem a better prospect.
Nor do I see how the various central banks can justify a pause in rate rises, at this point, but nor will they go in hard, that would be folly.
This Fed has made enough mistakes already.




