Fallen Emperor?
With almost two thirds of global equity markets represented by the US, the fall in the dollar so far this year is quite dramatic, and for many investments, more important than the underlying asset.
UK retail investors are especially exposed to this, as although Jeremy Hunt (UK Chancellor) may not notice it, the US is where most UK investors went, when his party’s policies ensured the twenty-year stagnation in UK equity prices.
While Sunak continues to pump up wage inflation, which he claims, “won’t cause inflation, raise taxes or increase borrowings” Has he ever sounded more transparently daft? Sterling, knowing bare faced lies well enough, then simply drifts higher. Markets know such folly in wage negotiation can only lead to inflation and higher interest rates.
We noted back in the spring, in our reference to “dollar danger” that this trade (sell dollar, buy sterling) had started to matter, and we began looking for those hedged options, and to reduce dollar exposure. To a degree this turned out to be the right call, but in reality, the rate of climb of the NASDAQ, far exceeded the rate of the fall in the dollar.
While sadly the other way round, a lot of resource and energy positions fell because of weaker demand and the extra supply and stockpile drawdowns, which high prices will always produce. But that decline was then amplified by the falling dollar, as most commodities are priced in dollars. So, a lot of ‘safe’ havens (with high yields) turn out to have been unsafe again.
The impact of currency on inflation
Currency also has inflation impacts. Traditionally if the pound strengthens by 20%, then UK input prices fall 20%. The latest twelve-month range is from USD1.03 to USD1.31 now, a 28% rise in sterling.
In a lot of the inflation data, this is amplified by a similar 30% fall in energy, from $116 to $74 a barrel for crude over a year. In short, a massive reversal in the double price shock of last year. In fairness this is what Sunak had been banking on, and why the ‘greedflation’ meme is able to spread. But while that effect is indeed there, other policy errors clearly override and mask it.
A Barrier to the Fed.
In the US we expect the converse, rising inflation from the falling currency, maybe that is creeping through, but not identified as such, just yet, as price falls from supply chains clearing lead the way, but it is in there.
Finally, of course, this time, the dire performance of the FTSE is probably related to the same FX effect on overseas earnings assumptions. Plus, the odd mix of forecast data and historic numbers that we see increasingly and idiosyncratically used just in the UK. If the banks forecast a recession, regardless of that recession’s absence, they will raise loan loss reserves, and cut profits, even if the reserves never get used.
Meanwhile, UK property companies are now doing the same, valuing collapsing asset values on the basis of the expected recession, and not on actual trades. So, if you have an index with heavy exposures to stocks, that half look back, half reflect forward fears, it will usually be cheaper than the one based on reality.
Why so Insipid?
OK, so why is the dollar weak? Well, if we knew that, we would be FX traders. But funk and the Fed’s ‘front foot’ posture are the best answers we have, and both seem likely to be transient too.
If the world is saying don’t buy dollars, either from fear of the pandemic or Russian tank attacks or bank failures, that’s the funk. As confidence resumes and US equity valuations look more grotesque, the sheep venture further up the hill and out to sea. To buy in Europe or Japan, they must sell dollars.
The VIX, in case you were not watching, has Smaug like, resumed its long-tailed slumber, amidst a pile of lucre.
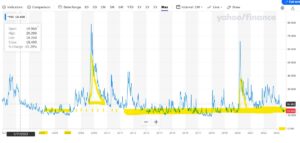
From Yahoo Finance CBOE Volatility Index
So as the four horsemen head back to the stables, the dollar suffers a loss.
The Fed was also into inflation fighting early; it revived the moribund bond markets, enticed European savers with positive nominal rates, (a pretty low-down trick, to grab market share) and announced the end of collective regal garment denial policies. But having started and then had muscular policies, it must end sooner, and perhaps at a lower level. So that too leads to a sell off in the dollar.
Where do we go instead?
So where do investors go instead?
In general, it is either to corporate debt, or other sovereigns. Japan is not playing, the Euro maybe fun, but not so much if Germany is getting back to normal sanity and balancing the books again. So, the cluster of highly indebted Western European issuers are next.
Sterling now ticks those boxes, plenty of debt, liquid market, no fear of rate cuts for a while, irresponsible borrowing, what is not to like?
For How Long
When does that end? Well, the funk has ended. You can see how the SVB failure caused a dip in the spring, but now the curve looks upward again. Although fear can come back at any time, as could some good news for the UK on inflation. However even the sharp drop the energy/exchange rate effects will cause soon, leave UK base rates well south of UK inflation rates.
So, every bit of good news for the Fed, is bad news if you hold US stocks here.
How high and how fast does sterling go?
Well, it has a bit of a tailwind, moves like any other market in fits and starts, but could well go a bit more in our view. Oddly the FTSE would be a hedge (of sorts).