This week has included a major but baffling fixed interest event in London. And we include some thoughts on the novelty of a conservative prime minister for the Conservative party – but first, the shape of the coming recession.
Who Survives in the Coming Recession?
It may help to see this recession, as just the reversal of the COVID boom, paid for with debt and deeply inflationary; in which case what should it look like? The ultimate aim will be to unlock labour markets, where we said (in our newsletter of 20-3-21) that COVID would do most harm.
Unlike traded goods or commodities or liquid assets, there is no simple snap back available without pain, because labour pricing is inflexible downwards. Indeed organised labour has worked hard to embed that inflexibility, notably in minimum wage laws, and the crippling of the hated gig economy.
Certain capital assets too are stranded and inflexible, but probably not most commercial (or residential) rents. Large single purpose buildings may be vulnerable and we feel, so is quite a lot of owner occupied residential property, whereby recent unearned gains will now need reversing.
Labour costs have two available paths. Either the 40% of working age adults who have now withdrawn from the labour market must (in some measure) return. It is their ongoing withdrawal post COVID that has hurt most. While COVID has also created (mainly in the public sector) a lot of extra staffing that is hard to step back from, especially in healthcare, which further depletes the available labour pool, and must also be reversed. Reducing labour taxes also helps.
Possible business failures
If not, there may instead need to be widespread private sector business failures. The third option, a speeding up of capital investment to substitute for labour, has somehow failed to be either fast enough or effective enough. It seems just too hard for businesses to predict demand paths, to commit to such expenditure. Cap ex is all about confidence, which is absent.
How then to measure if this labour reset finally happens? Well it looks as if job creation will need to go into reverse, with a net two quarters (at least) of contraction. There are plenty of businesses to fail, speculative and derivative loss making tech for a start, retailers of goods who over extended in the supply chain inspired boom, service sector spaces, where the current surge has drawn in capacity well in excess of long run demand, will all get hit.
As will everyday businesses, that have net margins that can’t withstand the double figure interest rates demanded of sub prime (i.e. now most SME) borrowers.
Paint that template over where the most savage equity falls have already happened, it fits quite well. But it is by no means universal, if IP, not labour matters, or labour can be off-shored, it is in a better place.
Although as jobs disappear, so the strain reaches further into total consumption and demand.
Fixed or Floating.
What of fixed income? Well we took the view early this year that you can’t stand in the way of an avalanche, unless you hope to surf it. So we kept clear, and still are.
Source : this page
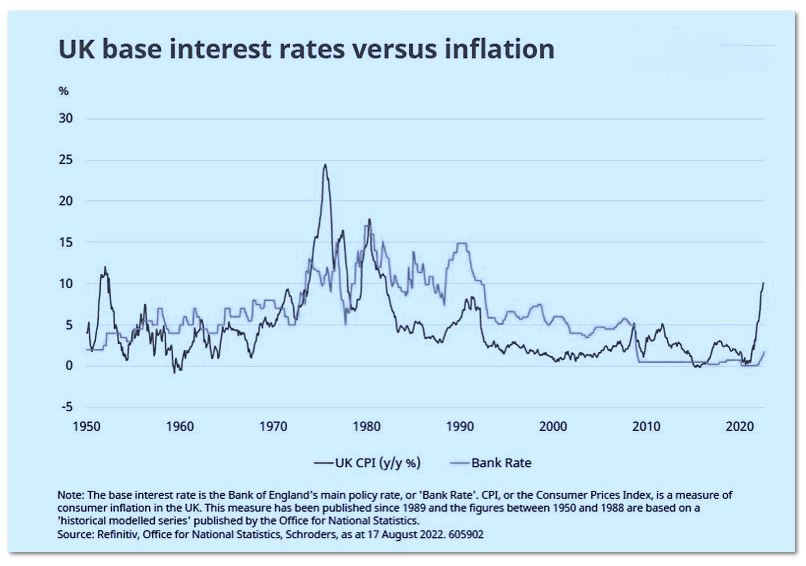
It was a very well attended fixed income conference in London this week, so credit is clearly back into portfolios, big time. My worry was the Table Mountain (or Brecon Beacons or Grand Canyon) graphs. All of which were steep sided, but flat topped, and on all of which, just now, is the exact point when lungs bursting, you climb the last butte, to see a vast sunlight upland.
Really? Why? No idea, but somehow the collective belief is rates top out circa 4% and then fall.
Certainly not if they mirror the inflation path (see above), that gap is now vast twixt interest rates and inflation; it will close – it has to. However we see more rises, not a near term peak and also far slower falls, than the market does. Reason? It is labour inflation that now drives it, and it won’t roll over soon.
Unless that is, the rate rises so far have done real damage and rates are then cut to mitigate a severe recession. If that’s the expectation (and it may be) you really don’t want equities at all, not even energy, the year’s bright spot.
So the question is, are high yield bonds now cheap?
Well yes, and quite attractive; defaults at the rate now implied, are unheard of. But if that odd plateau graph of rates is wrong, everything has yet to get even cheaper. That’s the rub. And that is why, for now, bar floating rate, secured, we are still not going into credit. And also because global interest rates must eventually align, so the dollar’s ongoing strength is a bad sign, as that will have to reverse too. This makes dollar assets themselves now dangerous.
The same dilemma is true for equities, yes, high quality, mid-size companies look cheap, the FTSE 250 is down some 20% in a year, almost as bad as the NASDAQ, whereas the FTSE 100 is modestly up (a distinction shared only with the Nifty 50). But again, we thought that value was emerging in the summer, but sadly not so; the market still sees a viscous earnings contraction ahead.
Which brings us back to employment, either it must fall, or participation must rise, and I fear we expect a fall, which seems more likely. This cycle, in the all important labour markets, still feels a long way from done.
New Broom
As for Truss, well talk of growth at the inept and hidebound Treasury is a nice change. As is that of getting the country working (spot on). This is core free market stuff. Has she the votes? Pretty sure she has, it was odd for the left wing of the party to eject Boris, who his actions showed was one of theirs. To unseat another leader would guarantee oblivion, so they must back her.
Worrying about fiscal rectitude, for a two year government, seems oddly implausible too. Yet she still fell prey to the old belief that governments (and higher tax) solve everything with her energy package, least of all can that solve demand based inflation. That is for Central Banks to do, and as ever, they are getting no help from the rest of government.
Does this suggest a big US rate hike this week? Not sure, we are much more seeing the end point as rather higher, than faster near term rises. We kind of think the Fed has made their point already.