DETONATION OR ROTATION
Two big market forces are at work just now, one is rotation out of the low interest rate winners, to wherever we go next, the other might be something more spectacular.
Enough of the market still sits in the “don’t know” category, to make everyone uneasy. The VIX is high.
So, what would cause the more explosive outcome? Traditionally higher rates divert more of the profits of indebted companies to banks and bondholders, so the theory goes, reducing dividends. Or at the more extreme level, this also makes refinancing debt harder.
This comes with a ‘second order’ impact, in that consumers or buyers also shovel more towards the banks, less towards the producers.
But none of this seems remotely likely yet, the world is awash with cash, and savings levels and interest rates have barely stirred from their COVID slumber.
Markets seem to be just talking about normalising, not slamming the brakes on.
Will we grow regardless of inflation?
The other big risk would be a failure of non-inflationary growth, which also seems unlikely. There are few practical signs of governments enacting the type of supply side restraint needed, we know. We still look for some self-restraint on how much governments seize in taxation; with high inflation taxes should be being cut, or thresholds systematically raised, but that’s also not happening.
The ‘idiot populace’ as curated by the media, constantly wants more supply side restrictions, greater consumption and lower prices, as if this was all somehow available; it is not. The worry here is that governments having messed up the big issues, give way to yet more populist demands for the impossible. At the same time, markets are also getting a little less keen to finance such nonsense or, being markets, raising the price at which they do so.
Well, all that is possibly true and has been happening for a while, but the old theory was that innovation was too fleet footed for any of that stuff to matter much. This is getting a bit tired, but broadly still seems to hold.
What if Ukraine does erupt?
So, the third detonator is in Vlad’s hands. Is a reverse Barbarossa coming down an autobahn near you? Well let’s assume yes, because he’s finally lost it. It is still fairly clear that if he steps onto NATO territory his army is in trouble, US and NATO airpower will rapidly outgun him. So, I discount that. But perhaps Ukraine does indeed end up like Belarus. China will support Putin, so the UN is irrelevant.
Then what? Well, a nation the size of Spain gets locked out of European commerce. Not important. Defence spend goes up? Well, some would say ‘about time’. Germany can decide to burn coal or nuclear or freeze, see previous answer. Come to that, so can we.
Given Russian gas must go somewhere, a bit like Iranian oil, it probably goes to China, which then trades it or cuts back its own Far East imports. Gas as we all know, can’t be stored for any useful length of time. Russia needs the earnings from it, so it will emerge on the market somewhere, at pretty much the current price.
It will be messy, it will create hard choices, but Russia is well on its way to autarky already, it can certainly live without dollars. Is this really a detonator? On its own, I doubt it.
Where is the rotation?
So, we still conclude all this market reaction is rotation, and it is out of overpriced US equities, where Biden created the biggest inflation bubble by far, and where interest rates are rising faster than elsewhere in the OECD. Hence, we see the hazard as mainly still on Wall Street, and to a lesser degree to the US economy. We’re looking at rising rates, a strong dollar, increased detachment from the global economy, and none of it helps earnings, but nothing is catastrophic either. The US (unlike the UK) wisely seized the chance to be energy independent.
But even so, we are not yet that concerned, valuations in the US are still extreme, as many sets of earnings seem to show, once the market looks at forward guidance, it shudders, and prices fall. A lot of built-in growth is needed to get price earnings ratios back down to earth, and that’s what’s being hit just now. To use a forty or fifty times earnings multiple, needs a lot of confidence about the future. That stretched temporal certainty is now lacking.
This is not that unusual for a rotation, but in that case, markets will bounce, and that will suddenly move a lot of funds off the side lines and back in. Where is that process now? Well going back to the Jan 27th low is causing some excitement. But we are not sure even that’s a disaster. Overall, the taking out of that and the October 2021 S&P low, won’t be fun, but the market still had a heck of a run up last year.
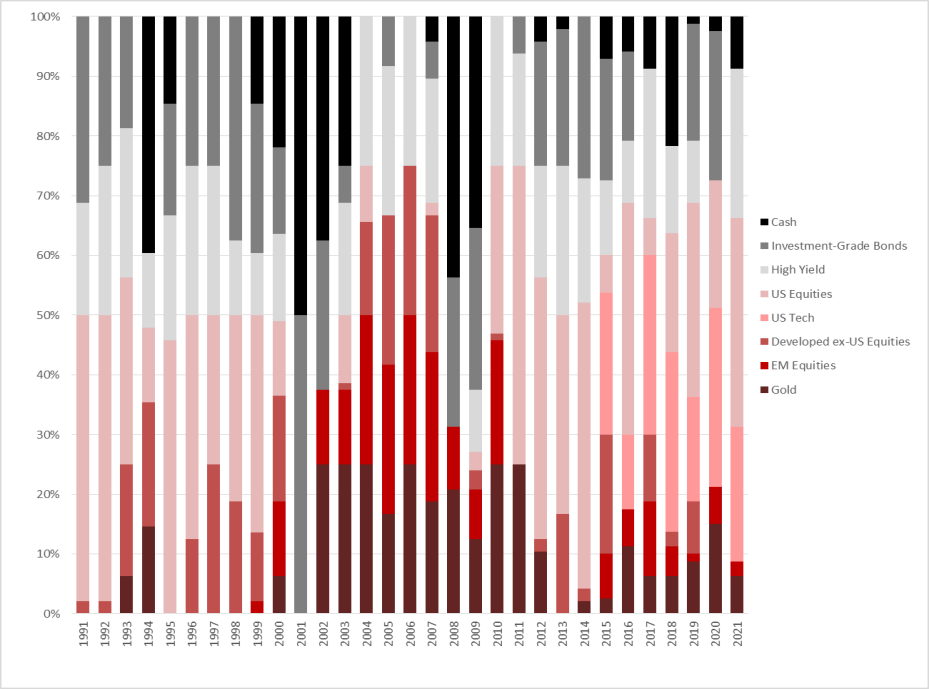
Have a look at where our MonograM investment model allocates funds based on momentum, over the last three decades, the US is absent for significant stretches. We rebalance monthly, the next one will be most interesting.
And inevitably, we do feel cautious too, but it is about levels, not wipe outs. Rotation not detonation.
Charles A R Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd
River Deep, Mountain High
Welcome back Mr. Powell - so what is a good response to impending inflation?
After nine months or more the newly reappointed Fed Chair conceded the blindingly obvious: we have an inflation issue, along with the equally transparent need to tighten monetary conditions to quell it. At least he’s fronted up to that, unlike the position in Europe.
What diverts us is what the right response is. Some things are perhaps obvious: gold at least in sterling terms now has positive momentum again. But there is a tremendous volume of liquidity to soak up still, while stimulus will keep being pumped in for a long time. But fixed interest just looks hopeless, credit quality is plummeting, rates are rising, and returns are poor, even in high yield.
Are we clear of COVID effects?
Nor are we really clear of COVID effects. We are yet to pass beyond all the “emergency measures”. So here in the UK, VAT is still reduced, commercial evictions banned, and government departments are still showing that odd mix of budget destroying costs and below normal productivity. So, spending pressure will stay elevated for a good while. Tax rises on corporate profits and on labour through National Insurance hikes, will therefore start to bite, well before the last variant has caused another pfennigabsatze-panik. (spike/trough related panic)
Markets have also been jittery. In general, the buying opportunities just after Thanksgiving have held, which is a good sign. The subsequent gyrations have (so far) indicated a good weight of money ready to buy the dips. But there is little doubt cash is fleeing the overhyped stocks, which are far more prevalent in the US, than in the UK. The shift out of basic commodities is also apparent. So, I would still expect enormous cash balances to build up into the year end in the banking sector, albeit maybe not always in the right places. Any Santa Claus rally will be strictly retail elf driven; the old man is self-isolating this year.
Characteristics of this inflation
Our view remains that the expected high inflation is systemic, simply because of the structural damage and inefficiency inflicted by COVID. So, it maybe transient, but multi-year transient. In this case while the seasonal moves down in energy prices will be a welcome relief, assuming Northern Hemisphere temperatures stay around seasonal norms (and that’s what mid-range forecasts are indicating) - it is not a solution to the inflationary pressures.
Nor do we see the any unwinding of the inventory super cycle caused by the holiday season and the ending of lockdowns, all at once, as having much beneficial impact on price levels.
Businesses all want inventory and will keep rebuilding it across their full ranges for a while. After all, right now holding stock has little financial cost attached.
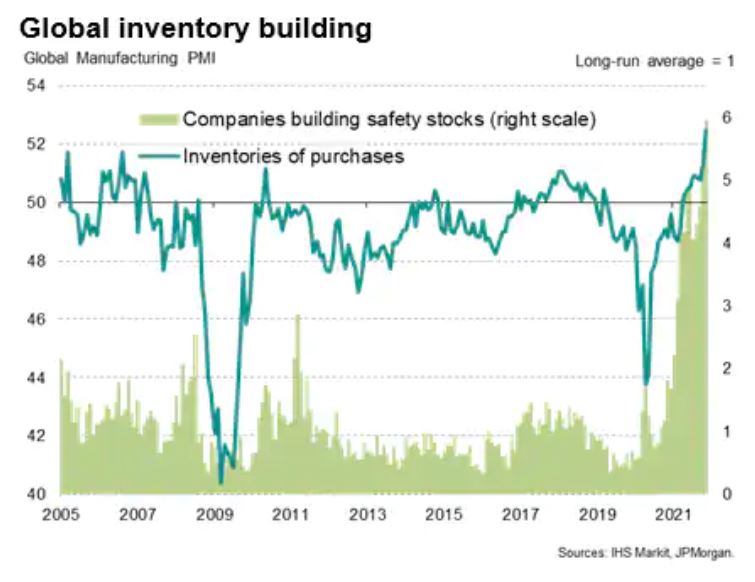
See this article published by Markit.
Most corporates are at heart squirrels; it won’t be easy to break a new habit.
So how should we play this?
The bigger issue is how to play this - the received wisdom is pile into the US, probably the NASDAQ, while having a side bet on bitcoin or some less disreputable alternatives.
That’s where most investors knowingly or otherwise have their funds.
NASDAQ may churn as dealers try to create some volatility, but the overall (and in our view inflated) levels will most likely remain.
This Omicron variant episode at least has halted the IPO madness, and the whole SPAC nonsense is washed up. Sadly, not a big surprise to see portly old London has just tried to catch a train that left the station last year.
The longer view
But it is a bubble we think - our icf economics monthly looks in more depth at how these played out the last couple of times. Not pleasant, but oddly familiar.
NASDAQ and Bitcoin may yet scale new peaks, but the river below is very deep. Perhaps that old affection for base gold is not just nostalgia?
Time for some year end reflection.
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management
Which is the Leviathan?
This is a week to ponder the role of private equity in portfolios, in what may be an early phase of a great investment and technological explosion. There seems to be no sign of higher interest rates and a stubborn refusal by Central Banks to care much about inflation. The talk of a UK raise always looked to us like a head fake which we ignored.
Spotting good and bad private equity
So first to private equity, a beast that comes in many guises, not all benign from an investor viewpoint. All liquidity fueled equity explosions come with a heavy loading of chancers; Bonnie and Clyde’s rationale for bank robbery remains valid.
Good private equity relies on management being superior to that of their targets. This can be in their analysis, their execution, their swiftness of foot or their innovation. All of this generally flourishes away from the hidebound inertia of many listed companies and their professional Boards of tame box tickers.
Bad private equity uses accounting tricks, the malleable fiction that the last price is the right price in particular, and the terrible phrase “discounted revenue multiple” which is a nice conceit for “never made a profit”. All of these share the same vice of management marking their own work.
So, we struggle with the likes of Scottish Mortgage and its little array of unquoted Chinese firms, the alphabet soup of non-voting share classes and love affair with management. Maybe they are that skilled, but nothing that looks like a real two-way market is evident to us, in many of these valuations. We have by contrast long admired Melrose Industries for their quite ruthless devotion to turning over their investments, good or bad and stapling executive pay to actual cash realizations paid to investors.
Where we stand – given our strategy
For an Absolute Return specialist there are added constraints: we want to hold under twenty positions altogether and all in ones we can sell tomorrow afternoon. And we like holdings where valuations are transparent, there is no gearing (there is usually quite enough in the private equity deals already), and you can pick them up for a fat double digit discount: oh, and we do like a yield too.
So, we are looking for big, listed options with hundreds of high-quality funds bundled together and for any yield, a bias towards management buy outs. We are certainly not at the venture capital end, with silly pricing, high fail rates, unrealistic managers, and not a decent accountant in sight and aspirations to change the world. Met those, invested in too many, and donated more shirts off my back than I care to enumerate to their serial failures and inexhaustible funding rounds.
But there are good things about Private Equity, one is that in a rising market, it can be like clipping a coupon. The accounting rules require them to be backward looking, so coming out of a trough they are typically reporting on valuations that are three or four months old, which in turn reflects business activity up to six months old. As they trade at a discount of typically 25% or so, you can buy today at a 25% discount to the value of the business they were doing in the spring. There are no guarantees, but for most, that was a lot worse than current conditions, so today’s price is simply wrong. This is a time machine that lets you buy now but pay at old prices.
Watch for built in volatility in private equity
These lags are complex, the reference points are often public market valuations, and so there is volatility built into them. While in an Absolute Return fund, not only are choices limited but the overall exposure must be too. However, in those rare purple patches of fast recovery and expansion they are excellent for performance.
What kills these bonanzas off is tight credit. In part they need debt for trade, but also their realizations rely heavily on it. A closed IPO market does them no good (just as they enjoy an exuberant one). That is a risk, as liquidity starts to tighten, that this will hurt, but as Powell and the Bank of England both showed, there is no political appetite for that just yet.
The UK and US on taming the leviathan
Indeed, Sunak’s UK budget yet again feels reckless, devoid of any discipline and with every department cashing in. Government spending is predicted to rise to 42% of GDP by 2026, a fifty year high. Healthcare alone is predicted to have grown by 40% in real terms since 2009 (both estimates from the oddly named Office for Budget Responsibility). At that level of loading, it is inching closer to hollowing out the entire budget and causing it to implode. (Leviathan was just such a creature “because by his bigness he seemes not one single creature, but a coupling of divers together; or because his scales are closed, or straitly compacted together” feels an apt description of this new giant state apparatus.)
But that gamble means there is no room to pay higher interest rates, or the economy will be reduced to a double-sided monster. The one face devoted to raising debt and levying taxes and paying interest, the other to feeding out of control public spending, with nothing left in between.
Thanks in a slightly odd way to a Democrat Senator, America has avoided throwing itself under that same bus, but with no effective political opposition the UK is now powerless to resist. Sterling’s relentless decline from the summer high and a FTSE 100 index still below its pre-COVID peak signify what markets feel about all this.
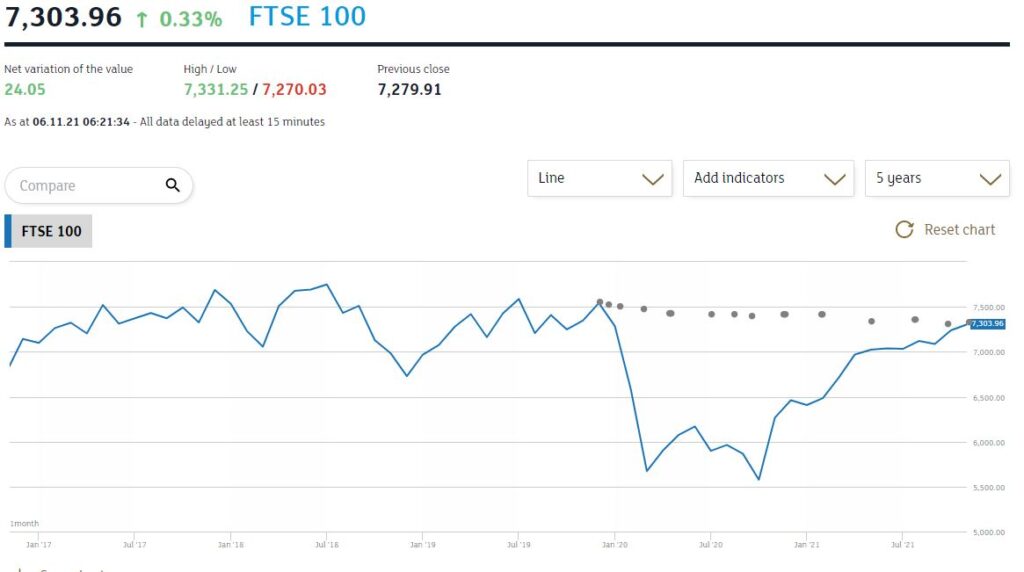
From the London Stock Exchange graph
So, while we were more bearish than we have been all year, in terms of asset allocation, at the end of October, we have yet to call time on the Private Equity cycle, that has provided such a powerful boost this year. It still feels good value to us.
Of course, we recognize too, that the populist fear is of the wealth creators and an opposing adoration for wealth consumption. Unlike politicians, however, we are tasked with producing real results not vapid dreams.
I guess we can each choose which to regard as the leviathan – the burgeoning state, or private equity.
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd
Thin ice skaters or savants?

Are we drifting out further from the shore of reason, confident we can slide gracefully back to safety, or do we have insight others lack? Perhaps rates just can’t rise, whatever the inflation rate? If so, they are a paper tiger. While in a week others have pondered the failure of UK investing during this century, we look at why our biggest bank seems to hate the country.
I’m talking about the economics prognostications from HSBC, our largest bank. Following an intellectually flawed change in accounting standards (yes, another one), on top of the insanity of “mark to market” comes the “predicted loan loss model”.
Now professional bankers (unlike those in fintech) don’t make loans to lose money.
So, the politicians have instead required them to assume that they do.
Do the regulators know the industry they’re regulating?
Imagine portfolio management where you assume a certain portion of your buys always fail. Might be true, but how? And if you admit you have to buy a certain number of your holdings to instantly lose money, what do your investors feel?
But although banks advance money on the basis of their credit committee assessments, the hordes of regulators deem some of it is immediately lost. Being rational people on the whole, the banks, not great fans of predicting the future (given their record), hire economists to do this for them.
Economists, as we know, actually know little, but they do build nice econometric models. The regulators, who know even less, tweak the models, the bank Boards (see above) also tweak them. Soon every model is so tweaked that the economists wonder why they bothered.
UK shown as the riskiest of places to lend
Which leads us to page 62 of the HSBC Interim Report. We read it, so you don’t have to. There on the excitingly named, but dull as ditch water section called “Risk” it is set out.
Now HSBC lends globally: Mexico, India, Vietnam, Peoples Republic of China. So, guess where “The highest degree of uncertainty in expected credit loss estimates” relates to? Apparently, the basket case to end all wicker weaving is . . . Yes, the UK.
How?
Well first up their ‘central scenario’ model sees the short-term average UK interest rates for the next five years, as 0.6%. Which at least is positive (unlike France, as they hate Macron even more), France (i.e., the Euro) rates are assumed to stay negative till after 2026.
This gloomy central scenario has a 50% chance, although for France it is a tiny bit better at 45%.
Now these are central estimates, but their “downside scenario worst case outcome” for the UK is heavily weighted, with a chunky 30% chance, and oops, France then gets a 35% chance of that disaster, neatly using up the slack just given to them, by the central scenario.
Oh, and there’s worse: house prices crater, double figure unemployment is locked in etc.
And that’s a combined 80% of outcomes sorted; for a bank, that is pretty near certain.
China compared to the UK and France
What about Mainland China, then, their biggest market, if you now include Hong Kong. Well like the US (75%), China is at a high (80%) central scenario certainty, with Hong Kong at 75%. The worst-case scenario for the PRC is ranked at just a measly 8%, the lowest of any of their major markets.
Call it impossible - a prediction that China can’t fail.
Well, if that’s what the economists believe, who are the dumb Board to argue? Well of course they can, to cover their well-appointed posteriors, they then chuck another couple of billion of extra reserves in on top of the doomsday forecasts.
So, you see the vortex, everyone, regulators, economists, non-executives are just adding to reserves, like the good old days.
Maybe they are right, but we are seeing very little sign of those incredibly low global interest rates for five years, negative in France, 0.6% in the UK, 1.1% in the US? Really? If they are right, the markets are wrong.
And it is not just technical, with a 35% chance of France hitting the worst-case scenario, no wonder the Board has shipped out their French operations to a fin tech start up, albeit one backed by private equity giants Cerberus. Not an outfit known for overpaying. With five-year rates at 1.1% the dash for cash in the US makes sense too, selling out of their retail side as well. While with a virtually nailed on, global leading, 5% five-year average GDP growth in the PRC included, surely time to expand there?
Their loan book does not bear out HSBC’s bullish estimates of Chinese infallibility
So it is with some trepidation that we look at their loan book, on Real Estate, in China. It must be massive? Certainly, markets apparently assumed so last week. But no, a paltry $6.336 billion, for HSBC that’s a rounding error. Luckily too, all rock solid, just $28m of reserves needed, although given their certainty that almost feels excessive. The Board probably slipped that bit in.
I have great admiration for HSBC, and for me personally it is a long-term hold, but I have much less regard for regulators and ‘economists’ models, about which only one thing is certain. They are wrong.
So, I try to just strip out the predicted loan loss nonsense, but it is still driving asset allocations, even when palpably false. It explains much of the last two year’s volatility in bank share prices and reported profits, it also justified the highly damaging dividend ban.
Yet the HSBC share price is still not much above 50% of its pre-COVID peak. Great investor protection that was, it hammered HMRC receipts too, for what? Based on what?
Does anyone challenge those weird scenarios internally at HSBC?
Is there really a 35% chance of France virtually collapsing in the next five years?
Or is this just part of cozying up to China? In which case as the IMF has shown, bankers accused of fiddling data for China, are not always seen as professionals and can lack credibility.
Regulators should not impose those odd fictions on real investment decisions either.
If they do real economies and yes jobs, suffer.
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd
A HARD RAIN
WHEN WILL MARKETS RESPOND?
Everything is in the end politics; it just takes a long route on occasion and rather like a frog in water, markets take time to realize that the pleasant feeling of warmth is a prelude to being boiled alive. We are well into the boiling phase, but how long before it all registers and an escape is finally attempted?
The purpose of politics seems ultimately to take an individual’s wealth and the fruits of their labour and give it firstly to the friends and allies of the confiscatory state and then use the remainder to buy votes. That bit does not ever really change, whoever is in charge.
So how does that truism impact markets on each side of the pond? Well, traditionally the UK state has been far greedier and done far more harm to the economy, than the US state has, which is why both GDP per capita is far worse than the US, and the FTSE has failed to rise, even in nominal terms, in two decades. Add back inflation and investing in UK PLC has been a long-term wealth destroyer. It enjoys that characteristic with the rest of Europe. As we have long said, lift the lid on any sensible UK pension fund, and you will find a lot of Apples inside.
In general, and this too is a platitude, well run dictatorships, especially those with access to world markets, do far better still, hence the rise of China. Of course, “well run” and “dictatorship” seldom sit well together, but nor do “populist” and “well run”. In general markets are not greatly in favour of either populists or dictators, feeling the rule of law is not something either care that much about. But by implication neither are voters now too fussed about laws either.
LONDON OR WALL STREET FOR THE REST OF 21? - THE BIGGER PICTURE
So, the investing question is whether the US, despite being increasingly under the control of the populist wing of the Democratic Party, is a better bet than the UK? Or do we have the capacity to process a bigger picture?

And of course, we need to ask whether China is better than both. So far, the US is finding Biden to be no worse than the populist wing of the Republican Party, and the UK is feeling rather baffled, given Boris constantly talks right but acts left.
Put like that our current sentiment, that Biden will cause more damage than Boris, is at the least contentious. So, we should look for the good in Boris and the bad in Biden, to help justify that call. Not an easy balance, but what makes it easier is the relative valuations. In particular of tech, where the US has moved ahead massively, so a lot of the question can almost be reduced to asking if Tesla is worth it? Or if it is, what is the motivating force to make it still more overpriced?
Boris seems to be trapped by the doctors and his inability to fathom numbers, into driving us into a permanent state of fear and welfare dependency, which will keep the UK steadily in long term decline. If he can break free of that populist vice, we might have a slim chance.
The omens are mixed, banning travel to Portugal (again) looks like the familiar science trap, but of course might be a reaction to the EU also banning wider travel from the UK to the EU just before that. Given our relations with the EU, that oddly seems more likely (if childish).
By contrast the US is now operating near normally, a stark contrast, as we remain in de facto lockdown, tied up in fiddly, unpredictable, illogical restrictions.
CULTURE WARS AS INDICATORS OF INVESTOR SENTIMENT
Both the Queen’s Speech setting out the legislative agenda for the year and the visit of Viktor Orban, the Hungarian premier, may have been light on substance (they were), but boy were they heavy with Tory symbolism, coming hard on the heels of the local election wins.
Much of that proposed legislation was to placate the grass roots, I seriously doubt laws on de-platforming (of both the living and the stone hewn) will make much difference, but the Conservative base feels it is high time the left got some mild resistance, in cultural matters. There has been very little of that for the last two decades.
I suppose the brutal bashing of Bashir is in the same category, although from my own experience a BBC journalist who did not lie and cheat their way to a non-existent story, would have been the truer rarity. Although in that they differ little from the rest of their breed, but defenestrations at the National Gallery and revolt at the National Trust, have been a long time coming and indicate a new degree of solidity and confidence. This is long overdue since Blair assiduously stuffed placemen into those organisations. Neither Cameron nor May did much about them, having their focus on higher things, it transpires.
Does it matter? Well not really, to markets, but it is a counter to the reckless spending, and the chilling clarity with which Boris famously expressed his view on business during Brexit, so is a straw in the wind. Maybe other things will change.
DEFUND THE DOLLAR?
What of Biden, well so far the US markets have taken slow comfort from the slender political majority, he holds, but the view is creeping in, that he really is going for broke, he is happy to unleash inflation, almost keen to do so, that letting Wall Street blow itself up, in the meme stock nonsense, and suppressing interest rates (which is vital if you are borrowing so much) and as a result trashing the dollar, is all fine, all part of the plan. Note the recent measures by China to prevent their currency appreciating too fast and by Putin (of all people) complaining at dollar fragility. Others may not attack it yet, but it increasingly looks like US policy.
Much of that perhaps matters little to Wall Street immediately; inflation makes you own real assets, bonds are now utter rubbish and so far, very little of US individual wealth is invested abroad. So, Wall Street almost inevitably drives itself up and that’s a hard tiger to dismount.
But it maybe matters more to us Europeans, who need to both believe that US overvaluations will persist and critically that the dollar will not weaken further.

So, in the end politics do matter, not now, not today, but how these contrasting styles evolve over the rest of the year, will be very important to how currencies and markets respond.
Getting it right for the second half involves a big call, this year, as it did last.
Flat markets are not always still markets.
Charles Gillams
Monogram Capital Management Ltd
06.06.21


